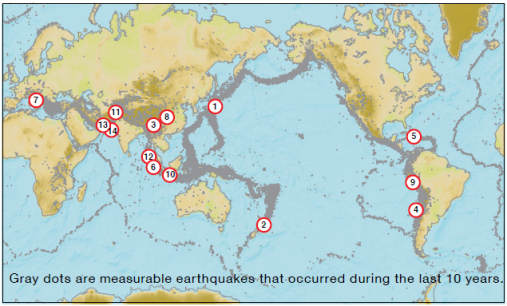
| |
Event
|
Magnitude |
Notable Effects |
Destruction |
| 1 |
Japan
March, 2011 |
9.0 |
Land dropped; tsunami wave heights up to 24 meters traveled up to 10 km inland devastating coastal communities. This was a triple disaster due to earthquake, tsunami, & radiation leaks from earthquake-damaged nuclear power plants. |
>10,000 killed; 17,000 reported missing; 125,000 buildings damaged; > 500,000 homeless |
| 2 |
Christchurch, New Zealand
February, 2011 |
6.3 |
Extensive ground shaking by the shallow earthquake in area of high population density. Liquefacton caused upwelling of > 200,000 tonnes of silt. |
>180 killed; 80% of water & sewer system damaged |
| 3 |
Yushu, China
April, 2010 |
6.9 |
At least 11 schoools destroyed in this sparsely populated region on the Tibetan Plateau. 12th century monastery and villages were severely damaged. |
2,698 killed; 12,000 injured 85% of buildings (11 schools) destroyed |
| 4 |
Offshore Maule, Chile
February, 2010 |
8.8 |
Shaking lasted 3 minutes and was felt in Peru, 2400 km away. Damage in Santiago. The earthquake generated a tsunami that devastated coastal communities. |
521 killed 370,000 homes damaged |
| 5 |
Port-au-Prince, Haiti
F
ebruary, 2010 |
7.0 |
The damage from the quake was more severe than for other quakes of similar magnitude due to both the shallow depth of the earthquake and the poor quality of construction. 250,000 residences and 30,000 commercial buildings destroyed. |
316,000 killed (May 1011, USAID adjusted figures to 46,000–85,000 killed.) 1,000,000 homeless |
| 6 |
Sumatra
December, 2009 |
7.5 |
Large buildings fell in the cities near the epicenter; landslides buried villages.Note: This is not the M9.1 earthquake of 2004; see below. |
1,115 killed 200,000 homes damaged |
| 7 |
L'Aquila, Abruzzo, Italy
April, 2009 |
6.3 |
Villages in the valleys suffered greater damage than medieval mountain hilltowns. L'Aquila was built on ancient lake sediments. The earthquke of 1703 destroyed the town of L'Aquila & killed 5,000 people. Felt in Rome, 60 km away. |
308 killed; 1500 injured 3,000–11,000 buildings damaged 65,000 homeless |
| 8 |
Sichuan Province, China
May 2008 |
7.9 |
At least 7,000 school buildings in Sichuan Province collapsed due to shoddy construction. Earthquake occurred in a poorer region where buildings are “just built; not designed” with earthquakes in mind, though they are common. |
69,000 killed; 5,000,000 homeless |
| 9 |
Chincha Alta, Peru
August, 2007 |
8.0 |
The city of Pisco suffered 85% of the buildings destroyed. 148 deaths occurred when the cathedral collapsed in the city's main square. |
519 killed; 85% buildings destroyed in Pisco & Chincha Alta. Many homeless |
| 10 |
Java, Indonesia
May, 2006 |
6.3 |
The earthquake's shallow depth was a major factor, but the scale of damage was made worse by failure to meet safe building standards. |
5,782 killed; 36,299 injured; 135,000 homes damaged. 1,500,000 homeless |
| 11 |
Pakistan
October, 2005 2 |
7.6 |
Landslides and rockfalls damaged several main roads cutting off access to the region for several days. Several villages destroyed. |
80,000 killed
32,000 buildings collapsed |
| 12 |
Sumatra
December, 2004 |
9.1 |
One of the deadliest natural disasters in history due to earthquake & tsunami pair.Third largest earthquake in recorded history. Vertical displacement of ~20 m over ~500 km length of the fault caused tsunamis with heights up to 30 meters. |
230,000 killed in 12 countries; 1,300,000 affected; Widespread water & food shortages |
| 13 |
Southern Iran
December, 2003 |
6.6 |
Caused by fault rupture on the Bam Fault. The effects of the earthquake were exacerbated by the use of mud brick as the standard construction medium. |
26,000 killed, 30,000 injured, 85% of buildings destroyed in the Nahrin area; 100,000 homeless |
| 14 |
India
January, 2001 |
7.7 |
Same site as the 1819 earthquake & proportionally the same number killed despite a seismic resistant building code. Liquefaction exacerbated shaking. |
20,000 killed, 167,000 injured 600,000 homeless |